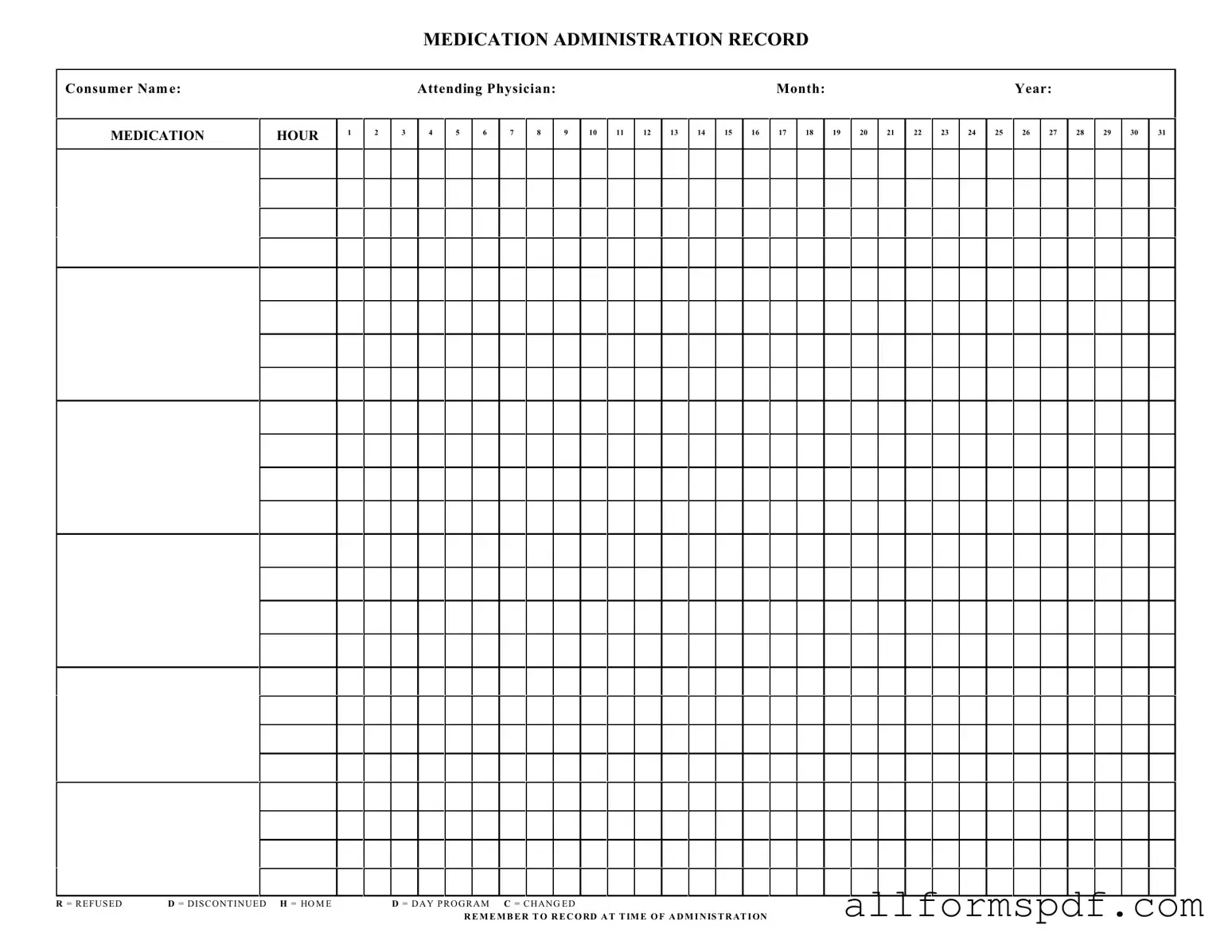
Fill Out Your Medication Administration Record Sheet Form
Medication Administration Record Sheet - Usage Guidelines
Filling out the Medication Administration Record Sheet is an essential task to ensure accurate tracking of medication administration. By following these steps, you can confidently complete the form and maintain a clear record of medication given to the consumer.
- Begin by writing the consumer's name at the top of the form where indicated.
- Next, fill in the attending physician's name in the designated space.
- Specify the month and year for which you are recording medication administration.
- Locate the section labeled MEDICATION HOUR and write down the hours during which medications are to be administered.
- In the columns provided, record the medications given at the appropriate hours. Make sure to note any specific details, such as the dosage or method of administration.
- If a medication was refused, write an R in the corresponding hour box. For medications that were discontinued, use a D.
- For medications administered at home, mark it with an H. If the medication was given during a day program, use a D.
- If there were any changes to the medication regimen, indicate this with a C.
- Finally, remember to record the time of administration clearly in the appropriate section.
Following these steps will help ensure that the Medication Administration Record Sheet is filled out correctly, providing an accurate account of the consumer's medication history.
Misconceptions
Understanding the Medication Administration Record Sheet (MARS) is essential for ensuring proper medication management. However, several misconceptions can lead to confusion. Here are eight common misunderstandings:
- MARS is only for nurses. Many believe that only nursing staff can fill out the MARS. In reality, any trained staff member involved in medication administration can use this form.
- It is unnecessary to record refusals. Some think that if a patient refuses medication, it is not important to note. However, documenting refusals is crucial for tracking patient compliance and safety.
- The MARS is only for prescribed medications. Many assume the form is limited to prescribed drugs. In fact, it can also include over-the-counter medications and supplements that the patient may be taking.
- Changes in medication do not need to be documented. Some believe that once a medication is changed, there is no need to record it. This is incorrect; documenting changes helps maintain an accurate medication history.
- The MARS is optional. A misconception exists that using the MARS is a choice. In reality, it is a necessary tool for ensuring compliance with medication administration protocols.
- All staff members understand how to use the MARS. While many may be familiar with the form, not everyone has received proper training. Ongoing education is vital for effective use.
- Recording time is not important. Some believe that the exact time of administration is irrelevant. However, timing can affect medication efficacy and patient safety, making it essential to record.
- The MARS is only a record of administration. Many think the MARS serves only as a log. In truth, it is also a communication tool among healthcare providers regarding patient medication management.
Addressing these misconceptions can enhance the understanding and effectiveness of the Medication Administration Record Sheet, ultimately improving patient care.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Medication Administration Record Sheet, it’s important to ensure accuracy and clarity. Here are some essential dos and don’ts to keep in mind:
- Do write clearly and legibly to avoid any confusion.
- Do include the consumer's full name and the date of administration.
- Do record the time of administration for each medication given.
- Do use the appropriate codes for refusal, discontinued, or changes in medication.
- Do double-check the medication dosages before recording.
- Don't leave any sections blank; ensure all fields are completed.
- Don't use abbreviations that could be misinterpreted.
Other PDF Forms
Wage and Tax Statement - Tax software often prompts users to enter information from their W-2 during filing.
Completing the Florida Horse Bill of Sale is essential for both buyers and sellers to ensure a smooth transfer of ownership, and for those looking for a template, you can find the necessary documentation at All Florida Forms, which provides resources tailored for these transactions.
Faa Aircraft Bill of Sale - Information on the form should match what is recorded with the FAA.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Medication Administration Record Sheet (MARS) is crucial for ensuring that patients receive the correct medications at the right times. However, mistakes can easily occur during this process. One common error is failing to accurately record the consumer's name. If the name is misspelled or omitted, it can lead to confusion and potential medication errors. Every detail matters, and accuracy in identifying the patient is essential for their safety.
Another frequent mistake involves the attending physician's name. This information is vital for tracking who prescribed the medications. If the physician's name is not included or is incorrect, it may complicate communication among healthcare providers. This can hinder the ability to address any issues related to the patient's treatment plan.
Additionally, many individuals overlook the importance of documenting the medication hour. Each medication must be administered at specific times, and failing to note these hours can result in missed doses. This oversight can have serious implications for the patient's health, especially if they are on a strict medication schedule.
Another common mistake is not using the correct codes for documenting medication statuses. For example, if a medication is refused, it should be marked with an "R." Mislabeling or failing to mark medications as refused, discontinued, or changed can lead to misunderstandings about a patient's treatment plan and can affect their overall care.
Lastly, many people forget to record the time of administration. This is a critical step in the process. Without this information, it becomes challenging to track when medications were given, potentially leading to double dosing or missed doses. Keeping accurate time records is essential for maintaining the integrity of the medication administration process.
Key takeaways
When using the Medication Administration Record Sheet form, it is important to adhere to the following key takeaways:
- Accurate Patient Information: Ensure that the consumer's name and the attending physician's name are clearly filled out at the top of the form.
- Timely Documentation: Record the administration of medication at the exact time it is given to maintain accurate records.
- Use of Abbreviations: Familiarize yourself with the abbreviations used on the form, such as R for Refused, D for Discontinued, and H for Home, to ensure proper communication of medication status.
- Monthly Tracking: Each month should be documented carefully, with attention to the specific days of administration to track compliance and any changes.